Monday, 15 September 2014
Different between Sales and Marketing: Definition of Marketing and sales
Saturday, 10 May 2014
Classifying new products: Types of Products: Six Kinds of Products
Six Kinds of Products
-By Booz, Allen and Hamilton (1982)
- New to the worlds (Totally new product like, evolution of mobile)
- New product line (mobile exiting now tablets)
- Addition to existing product line (mobile with flip )
- Improvement and revision to existing products ( mobile with new OS, or new features)
- Re positioning (Mobile phone for old age people: chocolate for old age people)
- Cost reductions (Now we offer our luxurious cell phone for common person )
Classifying New Product: Characteristics of new products
Characteristics of New Products
- Relative Advance: Seek to measure economic benefits
- Compatibility
- Novelty with an innovation
- More compatible a new product in with the existing system, its to be readily accepted
- At certain plant the new product may so resemble
- Complexity:
- define as degree of deficit associated with full understand of application of innovation
- Divisibility
- measure the extent to which it is possible to try an innovation before coming to final adoption/rejection decision
- it can have significant influence upon attitudes to wards a new product
- Communicability
- It's viral activity throughout the new product, new product purchase decision
All above factor measure objective factor
For subjective side: perception (important for product adoption)
Friday, 9 May 2014
Product Classification for Consumer Goods
Product Classification for Consumer Goods
For consumer goods, product divided in three category
- Convenience Goods
- Shopping Goods
- Specialty Goods
Shopping Goods: Those goods which consumer purchase in the process of selection and purchase on basis of suitability, quality, price, and style. I want to buy a cloth, For example, I'll check it out brand, take trial, asking to my brother/friends, looking price.
Specialty Goods: Those consumer good in which a significant group of buyer and make special purchase effort. I want to new Car, For example, I'll check out features compare with other brands, looking about price, asking users of cars, check out experts view about car.
Thursday, 8 May 2014
Types of Demand
Types of Demand
There are three types of Demand
- Effective demand: Customer financially sound and customer want product.
- Potential demand: Customer financially sound but customer don't want product.
- Latent demand: Customer not financially sound and customer want our product.
Loans, help to convert Latent demand to Effective demand
What is Product? (In Management)
What is Product?
The product is the object of the exchange process. The manufacture/supplier/producer offers to a potential customer in exchange for something which add or benefit to manufacture/supplier/producer.
Here something "something" is Money
Other than money, Barter (: exchange of things) or counter trade
Monday, 7 April 2014
Service Marketing: Four Categories of Services: know your service by Four Broad Categories of Services with examples
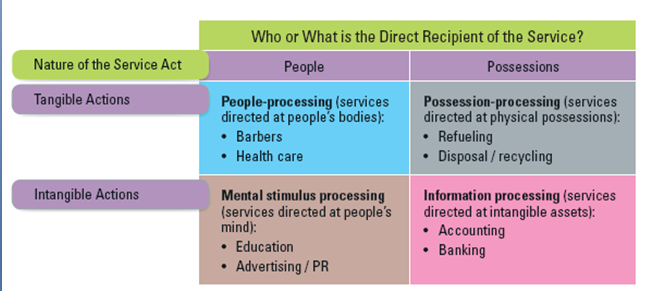
Four Broad Categories of Service
Though it, service provider can know which service.
This categories show how unwise it is to overgeneralize about services.
The mangers in particular service industry shouldn't fall in that trap of believing that their situation is unique and they have nothing to learn from any other service industry.
(Source: Service Marketing by lovelock)
There are total four categories,
Main two categories: Tangible and Intangible
In Tangible two part: People and Possession
In Intangible two part: Mental Stimulus and Information
(1) People Processing
- The action/work/ service do on direct on people body, with equipment and without equipment
- A physical location where people or machines/ both, create and deliver service benefits to customers.
- In People Process service customer must prepare for co-ordination with the service operator, for example, Hair cutting, customer must follow instruction given by barber. Follow the instruction given by doctor during the check up patient body
- Time required of customers in people processing services varies widely. Customer satisfied after completed services, to reach his/her destination, satisfied his hunger or is now sporting clean and stylishly cut hair or has has a good night's sleep away from home or is now in physically better health
- Example of people processing
- Passenger transportation
- Health care
- Lodging
- Beauty Salons
- Physical therapy
- Fitness centers
- Restaurants/bars
- Barbers
- Funeral services
(2) Possession Processing
- The service directed at physical possession (work/action/service do on customer's physical good's)
- Customers are less physically involved with this type of service.
- Example of Possession Processing
- Freight transportation
- Repair and maintenance
- Warehousing/Storage
- Office cleaning services
- Retail distribution
- Laundry and dry cleaning
- Refueling
- Landscaping/gardening
- Disposal/recycling
(3) Mental Stimulus Processing
- The work/activity/service with effect human mind. (Intangible)
- In this service customer must investment of time and mental effort.
- It can be inventoried. For example, customer's favorite movies/songs download from source and can store in their own gadgets and use it when they want.
- Example of Mental Stimulus Processing
- Advertising/PR (Personal Relations)
- Art's and entertainment
- Broadcasting/cable
- Management consulting
- Education
- Information Services
- Music concerts
- Psychotherapy
- Religion
- Voice telephone
(4) Information Processing
- Information is the most intangible form of service output, but it may be transformed into more enduring, tangible forms such as letters, reports, books, CD-Roms, or DVDs.
- That are highly dependent on the effective collection and processing of information are financial service and professional services such as accounting, law, marketing, research, management consulting, and medical diagnosis
- Example of Information Processing
- Accounting
- Banking
- Data processing
- Data transmission
- Insurance
- Legal services
- Programming
- Research
- Securities investment
- software consulting
Friday, 4 April 2014
7 P's : Service Marketing Mix: 7 P's of Service Marketing
Service Marketing Mix: 7 P's
Product:
- Service products are heart of the service marketing.
- Marketing mix begins with creating a service concept that will offer value to target customers and satisfy needs better than competing alternatives.
- Service product consist of a core and supplementary service element
- Core product meet primary need
- Supplementary element help to use the core product / add value on core product
Place:
- Delivering product element to customers involves decisions
- Delivery decision: Where; When; How
- Delivery may involve use of physical or electronic channel
- speed and convenience of place and time have become important determinants of effective service delivery
Price:
- Payment is play central role in marketing
- It is facilitating a value exchange between the firm and its customers.
- For customer point of view, price is key part of the costs they must incur to obtain wanted benefits.
- Revenue management is an important part in pricing
- Identify and minimize non-monetary cost incur by user: (time; expenditure; waiting; physical effort; negative sensory experiences.)
Promotion:
- Promotion is nothing but communication between manufacture and customer
- This component plays three vital roles
- Providing information and advice
- Persuading target customers of the merit of a specific brand or service product
- Encourage customer to take action at specific time
- Communication is educational for new customer
- Communication can be done by individual or in wide array
- individual: salespeople, front line staff; websites
- wide array of advertising media
Process:
- Customer are often involve in the process, especially when acting as co-producers.
- Creating and delivering product elements requires design and implementation of effective processes.
- Badly design process -
- slow
- ineffective service delivery
- wasted time
- disappointing experience
- Difficult to make sure that front-line staff do their job well
Physical Environment
- Service firms need to mange physical evidence carefully
- Because it can have a profound impact on customers' impressions
- Physical evidence are-
- Building
- Landscaping
- Vehicles
- Interior furnishing
- Equipment
- Staff Members' Uniforms
- Signs
- Printed materials
- Other visible cues
- This all provide tangible evidence of a firm's service quality
People
- Finally, in service always require direct interaction between customers and contact personnel.
- This interaction influences how customers perceive service quality.
- Service quality/customers' satisfaction depends on front-line staff
- Therefore, successful service firm give significant effort to recruiting, training, and motivating employees
Thursday, 3 April 2014
Powerful Forces Which Affect Service Economy
Powerful Forces are Affect Service Economy
There are basically 5 major factor which affect service economy
1st one Government Policy:
- Changing regulations: government change it's policy, putting restriction on new entry or minimize the use of certain product.
- Privatization: it's effect economy of the country and service industry also
- New rules to protect customer employees, and the environment: Suppose government found that some bad contain in pizza making, and they make restriction to make, buy or sell pizza. It's big effect on food service chain. In India, there is restriction to do advertisement on favor of smoking so ad agency lost their biggest client of all company who making cigarette.
- New Agreement on trade in Service
2nd one Social Changes:
- Rising consumer exception: service is basically performance, every consumer demand good service then others. their exception increase.
- More affluence: standard of living is increase, that's lead to more better performance
- more people short of time: now a days consumer need fast process. For example, fast delivery, fast performance of service
- increased desire for buying experiences vs. things
- rising consumer ownership of computers, cell phones, and high tech equipment: This lead to update or change the service process
- Easier access to more information: develop website, connect with internet, 24X7 customer service
- growing but aging population
- Push to increase shareholder value: company always looking to investor/shareholder value
- Emphasis on productivity and cost savings
- Manufactures add value thorough service and sell services
- More strategic alliances and outsourcing
- Focus on quality and customer satisfaction
- Growth of franchising
- Marketing emphasis by nonprofits
4th one Advances in IT (Information Technology)
- Growth of internet
- Compact mobile equipment
- wireless networking
- Faster, more powerful software
- Digitization of text, graphics, audio, and video
5th one Globalization
- More companies operating on transnational basis
- Increased international travel
- International mergers and alliances
- Offshoring of customer service
- Foreign competitors invade domestic markets
(Source: Service Marketing by Lovelock)
Wednesday, 2 April 2014
Definition of service, marketing point of view
Definition of service, Marketing point of view
Definition of Service:
"without take ownership of any physical element serve, labor, professional skill, facilities, networks, and systems with exchange of money, time and effort to customers expect to obtain value from access"
"Services are an economic activities offered by one party to another, most commonly employing time-based performances to bring about desired results in recipients themselves or in object or other assets for which purchases have responsibility" (source: service marketing by chripstoper Lovelock)
Elaborate
Service As a-
Economic Activities: In marketplace, buyer and seller exchange of value
Performance: perform the activity; seller perform activity for buyer
Result: variety of value-creating element, without taking ownership of physical element, exchange money, time and effor
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)